
Here are the most common examples of encryption. There are several types of encryption, each developed with different needs and security needs in mind. A private key, which is not shared, decrypts the data. A public key, which is shared among users, encrypts the data.

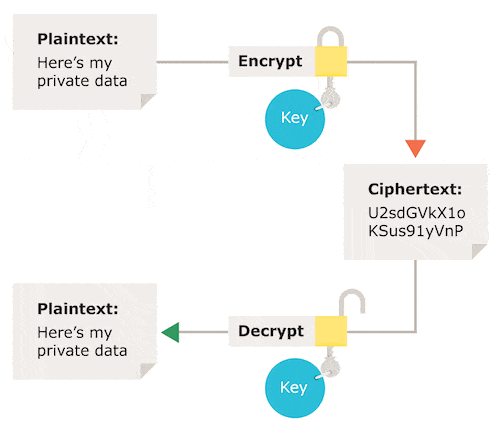
How does encryption work?Įncryption is the process of taking plain text, like a text message or email, and scrambling it into an unreadable format - called “cipher text.” This helps protect the confidentiality of digital data either stored on computer systems or transmitted through a network like the internet.

It’s nearly impossible to do business of any kind without your personal data ending up in an organization’s networked computer system, which is why it’s important to know how to help keep that data private.Įncryption plays an essential role. Vast amounts of personal information are managed online and stored in the cloud or on servers with an ongoing connection to the web. It helps provide data security for sensitive information.

Encryption is the process that scrambles readable text so it can only be read by the person who has the secret code, or decryption key.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
